In the rapidly evolving landscape of the job market, staying ahead of the curve is crucial for both individuals and organizations. The World Economic Forum’s Future of work 2023 report offers invaluable insights into the seismic shifts underway and the skills that will be paramount by 2027. This comprehensive report serves as a compass, guiding us through the uncharted waters of the evolving employment landscape. In this article, we’ll delve into the report’s core findings and explore how organizations are responding to the challenges it presents.

Winds of Change: The Shifting Skills Landscape
The report paints a vivid picture of a world where technology advances at a pace that outstrips traditional training and future of work methods. This acceleration leads to disruptions in the job market, with approximately 44% of workers’ core skills expected to be disrupted between now and 2027. The urgency for individuals and organizations to adapt becomes glaringly evident.
Sailing Toward Success: Top Skills in 2023
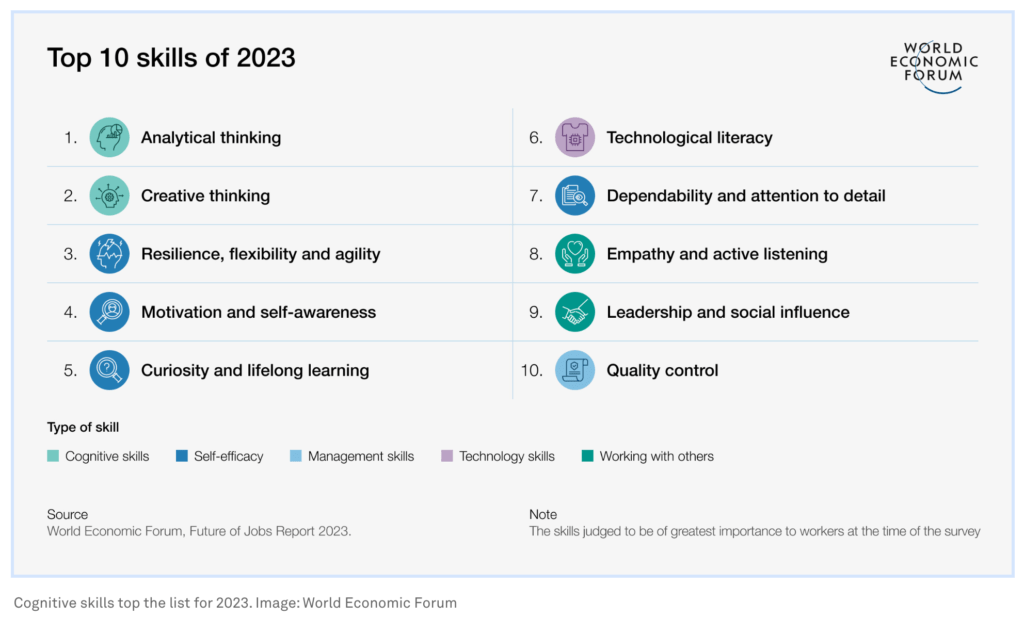
In 2023, cognitive skills take center stage, forming the bedrock of professional success. These skills include:
| Cognitive Skills | Self-Efficacy | Management Skills | Tech Skills | Working with Others |
| Analytical Thinking | Resilience, Flexibility & Agility | Quality Control | Tech Literacy | Empathy & Active Listening |
| Creative Thinking | Motivation & Self Awareness | Leadership & Social Influence | ||
| Curiosity & Lifelong Learning | ||||
| Dependability & Attention |
Cognitive Skills and Future of Work
In the dynamic landscape of the future of work, cognitive skills are essential. Let’s explore analytical thinking, creative thinking, and self-efficacy.
- Analytical Thinking: Analytical thinking involves systematically examining information, breaking down complex problems, and making logical evaluations. Key aspects include:
- Problem-Solving: Vital for dissecting complex issues and crafting effective solutions.
- Data Analysis: Crucial for extracting insights and supporting data-driven decision-making.
- Critical Decision-Making: Offers structured approaches for uncertain situations.
- Continuous Improvement: Encourages refinement, especially valuable in innovative industries.
- Creative Thinking: Creative thinking means generating innovative ideas, envisioning unconventional solutions, and adopting fresh perspectives. Key facets encompass:
- Innovation Catalyst: Challenging norms, introducing groundbreaking ideas, and identifying hidden opportunities.
- Adaptability: Thriving amidst change and uncertainty, excelling in exploring new possibilities.
- Collaborative Problem-Solving: Contributes diverse ideas within teams, fostering collective innovation.
- Entrepreneurship: Frequently leads to entrepreneurial ventures, addressing emerging market needs.
Self-Efficacy; It is an individual’s belief in their ability to succeed, influencing behavior, choices, and motivation., let’s explore its role in the future of work:
- Resilience, Flexibility & Agility: In the context of the future of work, resilience is indispensable. Those who believe in their capabilities (self-efficacy) tend to bounce back from adversity more effectively. Flexibility and agility are vital, allowing self-efficacious individuals to adapt swiftly to new situations and changing job demands.
- Motivation & Self Awareness: Motivation plays a pivotal role in thriving amidst the uncertainties of the future of work. Those with self-efficacy are highly motivated, understanding that their efforts are instrumental in achieving success. Self-awareness is equally critical, empowering individuals to make informed decisions and set realistic goals aligned with the evolving demands of their careers.
- Curiosity & Lifelong Learning: Curiosity fuels a desire for continuous learning and exploration, propelling self-efficacious individuals forward in the ever-changing landscape of the future of work. Lifelong learning is a commitment to personal and professional growth, recognized as a means to adapt to changing circumstances and remain relevant in chosen fields.
- Dependability & Attention to Detail: Dependability is highly regarded in the future of work. Self-efficacious individuals take ownership of their tasks, believing in their ability to meet commitments. Attention to detail is essential, even in the dynamic future of work, where accuracy and precision contribute to overall success.
Management Skills – Quality Control for the Future of Work:
Quality control requires strong attention to detail, problem-solving abilities, and effective communication skills to ensure products or services meet specified standards and customer expectations in the evolving future of work.
Tech Skills and Literacy in the Future of Work:
In today’s digital age, tech skills and literacy are fundamental. They empower individuals to thrive in the modern world, from basic computer proficiency to advanced programming and digital problem-solving.
Working with Others in the Future of Work:
Collaborating effectively within teams, sharing ideas, coordinating efforts, and contributing to common goals are paramount in the future of work.
- Empathy & Active Listening: Understanding and sharing others’ feelings, attentively hearing and comprehending what others say to build strong relationships.
- Leadership & Social Influence: Guiding, inspiring, and positively influencing others, fostering direction and persuading support for ideas or initiatives.
In the future of work, these skills and attributes, including cognitive skills and self-efficacy, will be vital for success in an ever-changing professional landscape.
Anchoring in Humanity: In-Demand Human Traits for Future of Work

In addition to cognitive skills, the report underscores the growing significance of human traits such as collaboration, leadership, and social influence. These qualities foster innovation and creativity in the workplace, as they enable employees to work effectively with others.
Navigating the Tides: Skills on the Rise

Analytical and creative thinking are expected to surge in importance for workers, with growth rates of 72% and 73%, respectively, over the next five years. This indicates an escalating need for reasoning, decision-making, and creativity in the workforce as automation continues to reshape industries.
Charting the Digital Course: Technology Literacy
Technology literacy is identified as the third-fastest-growing core skill. This reflects the increasing importance of understanding and harnessing technology in various job roles. As digital transformation continues to reshape industries, individuals with robust technology literacy will have a competitive edge in the job market.
Navigating the Training Seas: Challenges and Solutions
Despite the surging demand for skills, the report paints a sobering picture: only half of workers have access to adequate training opportunities. Six in 10 workers are projected to require training before 2027, highlighting a significant gap that requires immediate attention.
The Beacon of Data: AI and Big Data
AI and big data skills are poised for remarkable growth, with a projected 60% increase in demand by 2027. This underscores the paramount importance of data analysis and artificial intelligence across various industries. One of the key area where organisations are focusing on to get their employees skilled to be ready for future of work.
Leadership as a Guiding Star
While leadership skills rank ninth among the top skills for 2023, they are recognized as a growing need. Four in 10 corporate skills strategies will focus on upskilling workers in leadership, particularly in industries like automotive, aerospace, infrastructure, supply chain, transportation, and advanced manufacturing. Effective leadership is vital for navigating periods of change and uncertainty.
Sailing into the Future of Work: Organization Responses
To meet the challenges outlined in the Future of Jobs 2023 report, organizations are proactively taking a slew of measures:

1. Setting Sail with Training and Development
Investing Significantly: Organizations understand demands of future of work and related skills, and they are investing significantly in training and development programs. These initiatives encompass a wide array of learning opportunities, ranging from traditional classroom training to digital learning platforms and interactive workshops.
Customized Training: To cater to the diverse needs of their workforce, organizations are tailoring training programs to specific roles and career paths. This customization ensures that employees acquire the exact skills required for their current and future positions.
Continuous Learning Culture: Beyond periodic training sessions, organizations are fostering a continuous learning culture. They encourage employees to take ownership of their professional development by providing access to resources like e-learning modules, industry certifications, and educational subsidies.
2. Hoisting the Flag of Lifelong Learning
Promoting Self-Driven Learning: Organizations are encouraging employees to become self-directed learners. This means employees take the initiative to identify their skill gaps, set learning goals, and proactively seek out opportunities to acquire new knowledge and competencies and be ready to face future of work needs / challenges.
Flexible Learning Formats: Recognizing that employees have varying learning preferences and schedules, organizations offer flexibility in learning formats. This includes self-paced online courses, microlearning modules, and mentorship programs.
Recognition and Rewards: To reinforce the importance of lifelong learning, organizations are implementing recognition and rewards systems. Employees who invest in their own development and acquire new skills are acknowledged and often provided with advancement opportunities.
3. Navigating Collaborative Waters
Partnerships with Educational Institutions: Collaborating with educational institutions is an effective way for organizations to shape their workforce to meet future demands. These partnerships often involve curriculum design, guest lectures, and internship opportunities that align with industry needs.
Workforce Planning: Organizations work closely with educators to align the skills taught in academic programs with the skills needed in the job market as per future of work demands. This proactive approach ensures that graduates are well-prepared for employment upon completing their education.
4. Charting Practical Learning Courses
Internships and Apprenticeships: Many organizations are taking on interns and apprentices as a strategy to bridge the gap between theoretical knowledge and practical skills. These opportunities provide hands-on experience and often lead to permanent employment for talented individuals.
Job Rotation Programs: Some organizations have implemented job rotation programs, allowing employees to gain exposure to different roles within the company. This not only broadens their skill set but also helps identify potential future leaders.
5. Leveraging Technology for Personalized Learning
AI-Powered Learning Platforms: Technology, especially artificial intelligence, plays a pivotal role in personalized learning. AI-driven learning platforms assess individual skills, strengths, and areas for improvement. They then provide tailored content, ensuring that employees receive the most relevant training.
Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR): In industries where hands-on experience is critical, organizations are using VR and AR technologies to provide immersive training experiences. This is particularly valuable in fields such as healthcare, manufacturing, and aviation.
Gamified Learning: To make learning engaging and fun, organizations are incorporating gamification elements into training programs. Gamified modules often include challenges, rewards, and competition among employees, creating a dynamic learning environment for future of work.
6. Reskilling for a Resilient Crew
Identifying Skills for Future of Work: Organizations are proactively identifying which skills are at risk of becoming obsolete due to automation and technology advancements. They then provide reskilling pathways for employees to transition into roles that are less susceptible to automation.
Cross-Functional Training: Encouraging cross-functional training, where employees gain skills beyond their current roles, ensures a versatile workforce. This adaptability allows employees to seamlessly pivot when their current roles evolve or become redundant.
Certification Programs: Some organizations offer certification programs that formally recognize an employee’s proficiency in a specific skill or technology. These certifications can enhance an employee’s career prospects both within the organization and in the broader job market.
7. Supporting the Well-Being of the Crew
Mental Health Initiatives: Recognizing the toll that rapid change and uncertainty can take on employees, organizations are implementing mental health initiatives. These may include counseling services, stress management programs, and promoting work-life balance.
Physical Health and Wellness Programs: Promoting physical well-being is also a priority. Organizations often offer fitness programs, wellness challenges, and health screenings to keep their workforce healthy and resilient.
Flexible Work Arrangements: Flexible work arrangements, such as remote work options or flexible hours, contribute to employee well-being by providing a better work-life balance. This flexibility can reduce stress and improve overall job satisfaction, another must-haves for organisations to prepare themselves for future of work.
8. Fostering an Inclusive Crew
Diversity and Inclusion Training: Organizations are taking steps to foster an inclusive work environment by offering diversity and inclusion training. These programs aim to raise awareness of unconscious biases and promote equitable treatment of all employees. This has never been as crucial as it is today to ensure organisations are ready for future of work.
Diverse Hiring Practices: In addition to internal initiatives, organizations are adopting diverse hiring practices to attract a wide range of talents. This includes creating inclusive job descriptions, diverse interview panels, and outreach to underrepresented communities.
Employee Resource Groups: Many organizations have established Employee Resource Groups (ERGs) that provide support and networking opportunities for employees with shared characteristics or experiences. ERGs promote a sense of belonging and diversity within the workplace.
9. Staying the Course with Market Awareness
Market Intelligence Teams: Organizations have dedicated teams or functions responsible for monitoring market trends, especially regarding skill demands. These teams gather insights on emerging technologies, industry shifts, and competitor strategies these are key enabler to be inline with future of work needs.
Agile Workforce Planning: Armed with market intelligence, organizations adapt their workforce planning strategies accordingly. They adjust hiring, training, and reskilling initiatives to align with emerging skill requirements, ensuring that they stay competitive in the job market.
10. Embracing Flexible Work Models
Remote and Hybrid Work: The COVID-19 pandemic accelerated the adoption of remote and hybrid work models are must for the future of work. Many organizations continue to embrace these models, allowing them to tap into a global talent pool and adapt to changing workforce dynamics.
Flexibility in Working Arrangements: Beyond remote work, organizations are offering flexible work arrangements that cater to individual preferences. This includes options for flexible hours, compressed workweeks, and job-sharing arrangements.
Reference Resources
- World Economic Forum Future of Jobs 2023 Report
- Harvard Business Review: Why Skills Matter More Than Ever
- Deloitte Insights: The Future of Work
- McKinsey & Company: Reskilling in the Age of Automation
- MIT Sloan Management Review: The Role of Leadership in Navigating Change
- Forbes: The Benefits of a Diverse Workforce
These reference resources provide additional insights into the topics covered in this article and serve as valuable sources for those seeking more in-depth information on the future of work, skills development, and organizational responses to changing job landscapes.
FAQs: Navigating the Future of Work
FAQ 1: What Is the Future of Jobs 2023 Report, and Why Is It Important?
Answer: The Future of Jobs 2023 report is a comprehensive analysis by the World Economic Forum that provides insights into the changing job market and the skills that will be in demand by 2027. It’s crucial because it highlights the skills and qualities individuals and organizations need to navigate the rapidly evolving employment landscape effectively.
FAQ 2: How Can I Prepare for the Skills Disruptions Mentioned in the Report?
Answer: To prepare for skills disruptions, consider investing in continuous learning. Focus on developing cognitive skills like analytical and creative thinking, and embrace a culture of lifelong learning. Stay adaptable, build resilience, and be open to acquiring new skills throughout your career.
FAQ 3: What Should Organizations Do to Address the Skills Challenges Outlined in the Report?
Answer: Organizations should prioritize training and development, collaborate with educational institutions, offer practical learning opportunities, leverage technology for personalized learning, and actively reskill employees. Promoting employee well-being, fostering inclusivity, and staying market-aware are also crucial steps.
FAQ 4: How Can I Stay Informed About Emerging Job Trends and Skill Demands?
Answer: Staying informed about emerging job trends and skill demands requires regularly monitoring industry news, participating in professional networks, and seeking insights from market intelligence teams within organizations. Keep an eye on industry reports and be open to adapting your skills based on changing demands.
FAQ 5: What Role Does Leadership Play in Navigating the Future of Work?
Answer: Leadership is instrumental in guiding organizations through change and uncertainty. Effective leadership fosters a culture of adaptability, innovation, and continuous learning. It also plays a vital role in upskilling the workforce and aligning strategies with evolving job market trends.
FAQ 6: What Are the Key Implications of the Skills Disruptions Mentioned in the Report for Job Seekers?
Answer: The key implications for job seekers are the need to continuously upgrade their skills, embrace digital literacy, and focus on cognitive skills like problem-solving and creativity. Job seekers should also prioritize adaptability and the ability to learn new technologies and tools.
FAQ 7: How Can Educational Institutions Align Their Curricula with the Skills Demands Highlighted in the Report?
Answer: Educational institutions can align their curricula by actively engaging with industry experts, conducting regular skill gap assessments, and updating course offerings to reflect emerging skill needs. Collaboration with businesses can lead to internship and apprenticeship programs that provide students with real-world experience.
FAQ 8: What Are the Potential Benefits of Embracing Remote Work and Flexible Work Arrangements in Light of the Report’s Findings?
Answer: Embracing remote work and flexible arrangements can benefit both employers and employees. Employers can access a broader talent pool, reduce overhead costs, and adapt more easily to changing workforce needs. Employees gain increased work-life balance, reduced commuting time, and the ability to work in environments that suit their productivity.
FAQ 9: Are There Specific Industries or Sectors That Will Be More Affected by Skills Disruptions According to the Report?
Answer: Yes, according to the report, industries that heavily rely on manual or routine tasks are more likely to be affected by skills disruptions due to automation. This includes industries like manufacturing and some administrative roles. However, the impact can vary widely, and proactive reskilling efforts can mitigate disruptions.
FAQ 10: How Can Governments Play a Role in Addressing the Skills Challenges Highlighted in the Report?
Answer: Governments can play a significant role by creating policies that support lifelong learning, investing in education and vocational training, and incentivizing businesses to upskill their workforce. They can also collaborate with industries to identify emerging skill needs and foster economic resilience in their regions.
These FAQs provide valuable information for individuals and organizations looking to understand and address the challenges and opportunities presented by the changing world of work outlined in the Future of Jobs 2023 report.

1 thought on “Navigating the Future of Work: Key Insights from the World Economic Forum’s Future of Jobs 2023 Report”
Comments are closed.